NEWS CENTER
Recrystallization and its effect on structure performance
- Time of issue:2018-12-10 18:10
(Summary description)1. When the deformed metal during the recrystallization process is heated at a higher temperature, the elongated (or squashed) and broken grains will become new uniform and small through re-nucleation and growth due to the increased atomic diffusion capacity. The isometric crystal. This process is called recrystallization. After the deformed metal is recrystallized, the strength and hardness of the metal are significantly reduced, while the plasticity and toughness are greatly improved, and the work hardening phenomenon is eliminated. At this time, the internal stress disappears, and the physical and chemical properties are basically restored to the level before the deformation. The lattice type of the new crystal grains generated by recrystallization is the same as the lattice type before and after deformation.
Recrystallization and its effect on structure performance
(Summary description)1. When the deformed metal during the recrystallization process is heated at a higher temperature, the elongated (or squashed) and broken grains will become new uniform and small through re-nucleation and growth due to the increased atomic diffusion capacity. The isometric crystal. This process is called recrystallization. After the deformed metal is recrystallized, the strength and hardness of the metal are significantly reduced, while the plasticity and toughness are greatly improved, and the work hardening phenomenon is eliminated. At this time, the internal stress disappears, and the physical and chemical properties are basically restored to the level before the deformation. The lattice type of the new crystal grains generated by recrystallization is the same as the lattice type before and after deformation.
- Categories:Industry News
- Author:
- Origin:
- Time of issue:2018-12-10 18:10
- Views:
1. Recrystallization process
When the deformed metal is heated at a higher temperature, the elongated (or squashed) and broken grains become new uniform and fine equiaxed crystals through re-nucleation and growth due to the increase in atomic diffusion capacity. This process is called recrystallization. After the deformed metal is recrystallized, the strength and hardness of the metal are significantly reduced, while the plasticity and toughness are greatly improved, and the work hardening phenomenon is eliminated. At this time, the internal stress disappears, and the physical and chemical properties are basically restored to the level before the deformation. The lattice type of the new crystal grains generated by recrystallization is the same as the lattice type before and after deformation.
2. Recrystallization temperature
The temperature at which the deformed metal recrystallizes is a temperature range, not a certain constant temperature. Generally speaking, the recrystallization temperature refers to the lowest recrystallization temperature (Tre), usually a metal that has undergone a large amount of deformation (over 70%) of cold plastic deformation, and the lowest temperature at which it can be completely recrystallized after heating for one hour. Express. The minimum recrystallization temperature has the following relationship with the melting point of the metal:
T then = (0.35~0.4) T melting point
The temperature unit in the formula is absolute temperature (K). The minimum recrystallization temperature is related to the following factors:
(1) Pre-deformation The relative amount of plastic deformation before metal recrystallization is called pre-deformation. The greater the pre-deformation, the more crystal defects of the metal, the more unstable the structure, and the lower the minimum recrystallization temperature. When the pre-deformation reaches a certain level, the minimum recrystallization temperature of the metal tends to a certain stable value.
(2) The higher the melting point of the metal, the higher the minimum recrystallization temperature.
(3) Impurities and alloying elements Because impurities and alloying elements, especially high melting point elements, hinder atom diffusion and grain boundary migration, the minimum recrystallization temperature can be significantly increased. For example, the minimum recrystallization temperature of high-purity aluminum (99.999%) is 80°C, while the minimum recrystallization temperature of industrial pure aluminum (99.0%) has increased to 290°C.
(4) Heating speed and holding time. Recrystallization is a diffusion process and it takes a certain amount of time to complete. Increasing the heating rate will cause recrystallization to occur at a higher temperature, and the longer the holding time, the lower the recrystallization temperature.
3. Grain size of crystal grains after recrystallization
The grain size affects the strength, plasticity and toughness of the metal, so the production pays great attention to the control of the grain size after recrystallization, especially for those steels and alloys that have no phase change. The main factors affecting the grain size after recrystallization annealing are heating temperature and pre-deformation.
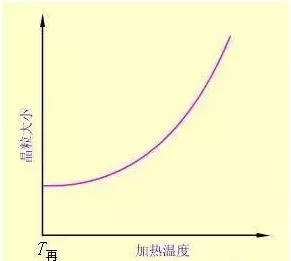
(1) Heating temperature The higher the heating temperature, the stronger the atom diffusion ability, the easier the migration of grain boundaries and the faster the grain growth.
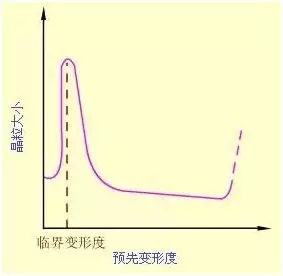
(2) The influence of pre-deformation degree of deformation degree is mainly related to the uniformity of metal deformation. The more uneven the deformation, the larger the grains after recrystallization annealing. The degree of deformation is very small, because it is not enough to cause recrystallization, the crystal grains remain unchanged. When the degree of deformation reaches 2-10%, a small number of crystal grains in the metal are deformed and the deformation distribution is very uneven. Therefore, there are few crystal nuclei generated during recrystallization, and the crystal grain size varies greatly, which is very conducive to the process of crystal grains. Grow up quickly, resulting in extremely coarse grains. The degree of deformation that causes abnormal growth of crystal grains is called the critical degree of deformation. In production, plastic deformation processing within the critical deformation range should be avoided as far as possible. After the critical deformation degree is exceeded, as the degree of deformation increases, the deformation of the crystal grains becomes more intense and uniform, and there are more and more recrystallized cores, so the crystal grains after recrystallization are getting smaller and smaller. But when the deformation is too large (approximately ≥90%), the crystal grain may grow abnormally again, and it is generally believed that it is constructed by deformation weaving.
Hot News

黄石山力科技股份有限公司
Sunny Technologies Incorporation Limted

Contact us
Add:No. 2, Guangzhou road, tuanshancheng Development Zone, Huangshi City, No. 101, Gaoxin 6th Road, Donghu New Technology Development Zone, Wuhan
Mail:spt@sunnychina.com.cn
Tel:156 7177 7755 / 027-59715061
Fax:027-59715060





